Utilized correctly, Agile is a fantastic tool. Breaking big software application jobs into smaller sized, actionable pieces offers an excellent method for IT groups to decrease shipment danger However when a business is confronted with a seriousness for modification, or a desperate requirement to get things back on track, its decision-makers can end up being susceptible to the misconception that Agile adoption can resolve whatever
Agile can stop being a valuable tool when the Agile “tail” starts to wag the business, leading decision-makers to ban jobs that do not fit nicely within the company’s changed criteria. At finest, blind adherence to a structure’s guidelines will produce a stilted administration that demoralizes staff member, one in which conferences and events are carried out for no higher function. At worst, Nimble myopia can hide larger issues such as an absence of management and innovative risk-taking.
In the lack of a structured method to run the risk of management, Nimble practices can obfuscate bigger, underlying concerns such as tech financial obligation, occlude overarching item vision, and lead item groups to focus just on fast wins. Simply put, ambiguous danger management obscures big-picture, innovative services. In an Nimble environment, the greatest danger dealt with by item leaders depends upon an old truism: Often it’s simple to forget the forest when you focus excessive on the trees.
Item supervisors must cultivate a tolerance for risk-taking by promoting bigger efforts that do not dovetail with an Nimble structure: Supporter for imagination and a clear and vibrant item vision to preempt the possibly inert administration that can accrete in a risk-averse environment.
It’s simple and appealing to put Agile on auto-pilot, just doing what a specific structure states. Pursuing something much better needs utilizing your own effort to put in more work, invest more time, and motivate more effort from management at every level.
Rooting Out Tech Financial Obligation: Believe Huge
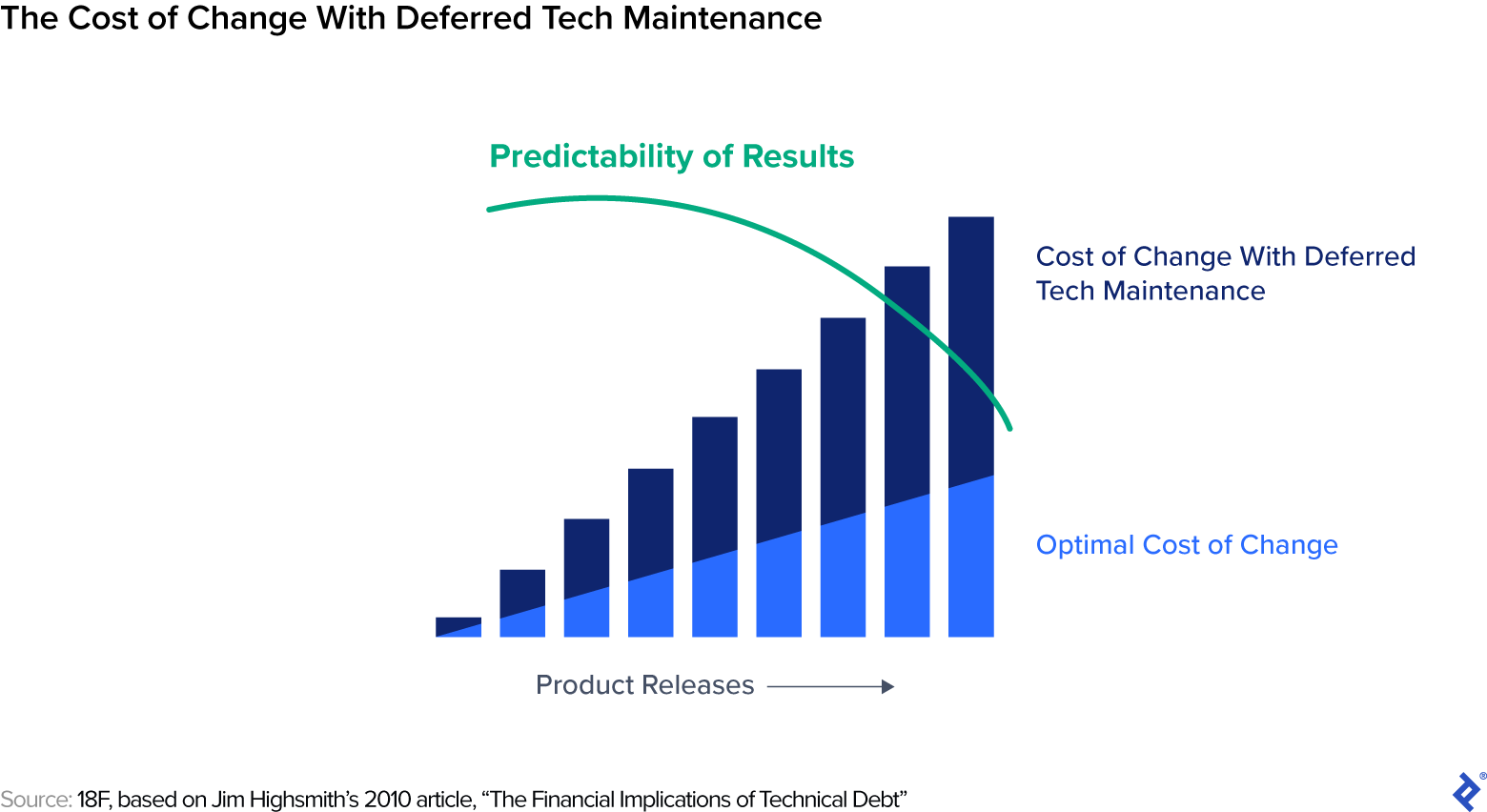
Among the very first casualties of the Agile veto takes place when bigger efforts like technical financial obligation are neglected. Technical financial obligation is an enormous and continuous job that can’t be fixed in a single sprint or managed in one user story. To make matters harder, tech financial obligation is an issue no one truly likes to address: It can be challenging to discuss the reasoning for resolving tech financial obligation to organization stakeholders who wish to see instant returns. Designers are frequently unpleasant approximating it; after all, recognizing technical financial obligation might provide the impression that they did their tasks badly. What’s more, item groups frequently do not have a appropriate location for it on their roadmap
On numerous jobs I have actually dealt with– numerous in e-commerce– core organization activities such as payments, order satisfaction, or shipping were encumbered technical financial obligation that avoided the application of much better services. Strained with a creaky facilities, a minimum of 2 of my customers picked to neglect the issue till the systems stopped working, triggering downtime and lost income. As soon as a system stops working, whether it’s a piece of software application or a cars and truck’s brake pads, the overall expense of repair work increases greatly
So why does this take place? In part due to the fact that the desire for a foreseeable roadmap and smooth Nimble procedure develops a predisposition towards Agile-suited activities and prevents severe conversations of larger concerns. Letting commitment to Agile figure out organization goals, instead of utilizing Agile as a tool to make organization goals run efficiently, has unhealthy results on business.
Dropping the Trees: Imaginative Damage
In my experience, business see imagination as associated with danger. Definitely they desire the advantages that come from imagination, however doing something brand-new may end in failure. A strongly risk-averse type of Agile, when permitted to affect organization choices, intensifies this issue.
For example, I have actually been faced numerous times with below average e-commerce funnels Typically, these funnels are weighed down with either style financial obligation or technical financial obligation and produced for an audience or personality that has actually altered considerably given that the item was very first launched. In these cases, the appropriate method forward would be to acknowledge the circumstance based upon the information, and introduce a significant UX job to look into brand-new personalities, craft a brand-new method, and reconstruct the funnel– in other words, to produce a completely brand-new funnel. Rather, what usually takes place is small tweaks occasionally, with a concentrate on iterative enhancements to an existing (extinct) funnel. This originates from the misdirected look for performance where none can be had, for jobs that nicely suit a sprint, and for little jobs that supply fast wins.
Often little models aren’t the ideal method to fixing an issue. In the software application market, increments work well– till a disruptor occurs If you discover yourself still making incremental modifications to a pager when Apple has actually currently opened an iPhone factory next door, you’re focusing so hard on the trees that you have actually forgotten the forest.
A Nimble Danger Management Structure: The Course Forward
The only remedy to anti-risk predisposition is to cultivate appropriate management that takes area for innovative danger management, utilizing Agile as a tool to lessen unneeded danger, not remove it.
For item supervisors, our task is to show management at the group level, and assistance management at the organizational level: Deal with stakeholders, item groups, and tech groups to make certain they comprehend and are lined up with the methods talked about listed below, which will keep your item group from diverting into a culture of overall danger hostility
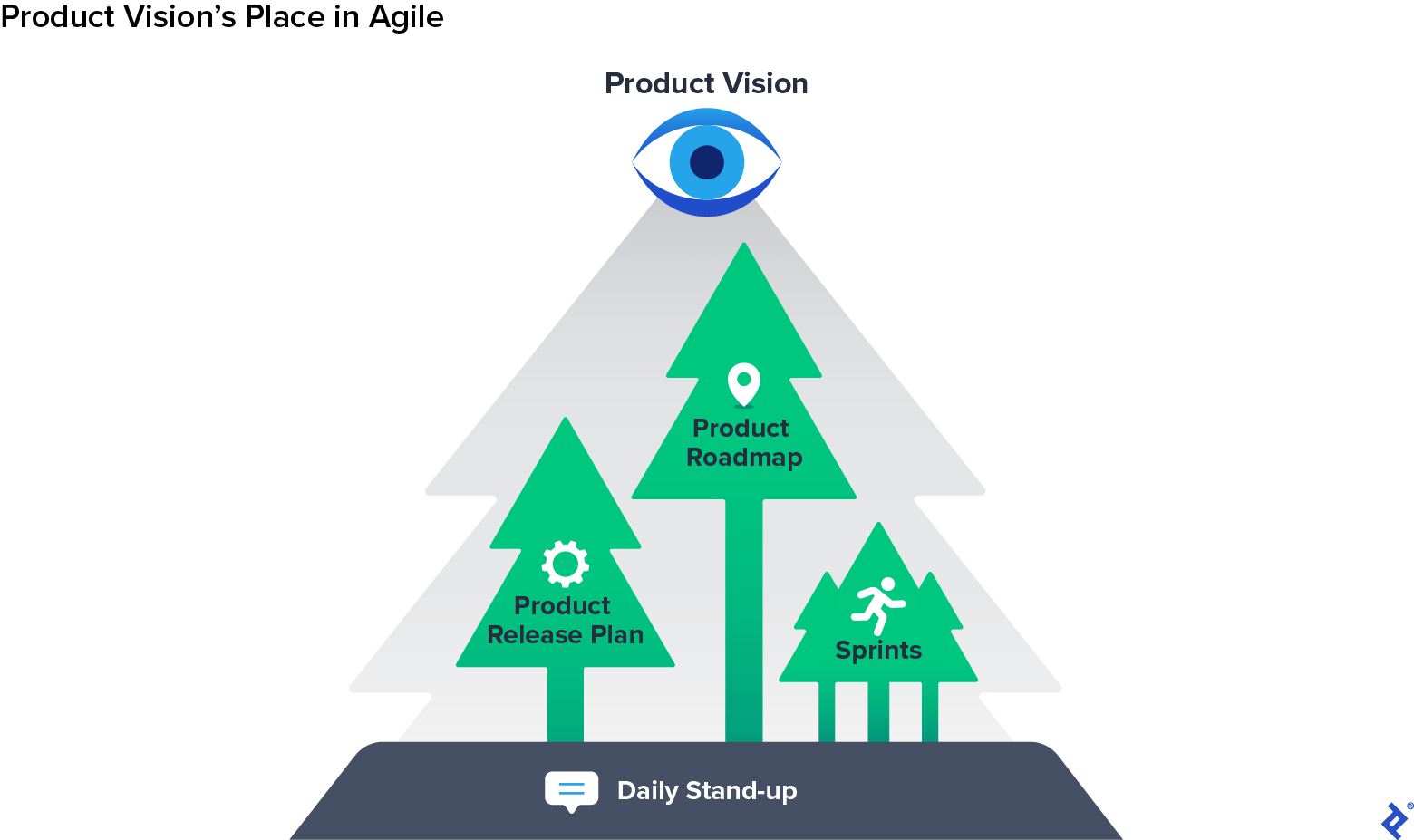
Keep a Clear Item Vision
Understanding and accepting that danger hostility can emerge in a Nimble age is currently a big initial step towards avoiding it from settling. The next action is to resolve issues brought on by an absence of management and ownership: An item vision should be assisted by somebody who supports it, safeguards it, and offers it internally within the company, pressing back versus rigidness and the impulse to thin down a strong method.
Preferably, the individual who owns the item vision must be somebody in the C-suite, possibly a creator, who takes obligation for keeping the concentrate on what you’re making and why– not simply how. However an item existence at the executive level is still a reasonably brand-new advancement The next finest case is having a vice president or Head of Item who has adequate autonomy and authority to break the present. If a ready-made champ of item vision does not exist at your business, you might need to put in some work to cultivate such an ally.
Usage efficiency metrics that make the case for your top priorities: A distinct set of KPIs can incentivize action over inertia. Individuals you’re attempting to win over have hectic schedules, so these metrics, just like information visualizations, must be couple of, basic, succinct, and clear to anybody evaluating them in the very first 30 seconds. As soon as you have your ally, the strong efficiency metrics you have actually offered will likewise serve to equip the item leader in their efforts.
Manage Information to Promote Big Efforts
An excellent engineering group currently comprehends the risks of leaving technical financial obligation unaddressed. However when they’re equipped just with technical details, their voices can be silenced or lessened by organization groups that focus too directly on the bottom line.
This is another circumstances in which having actionable information easily offered is important. The item supervisor, as somebody with a foot in both engineering and organization, can work as a channel of details, empowering the engineering group to make its case. For instance, if a KPI reveals the requirement to enhance test protection over a provided crucial system, or an OKR shows use concerns need to be solved within one month, these focus the conversation on technical financial obligation. Buffeted by a requirement to enhance these metrics, the engineering group can promote for a technical financial obligation job with decision-makers. Similarly, cynics have a much more difficult time putting such jobs on the back burner, a popular method for disregarding big however delayable efforts.
Support Imagination in a Risk-averse Environment
Imagination on a group does not simply take place, and disturbance does not come out of no place. Imagination requires to be supported and kept track of by a senior decision-maker. One method this can take place is on an individual level, by making an intentional option to take more time for more conversation with a more varied set of individuals. I have actually personally had circumstances where somebody from the customer-service group or an intern in operations proposed some really ingenious services that shocked both item and tech. However you’ll never ever hear those concepts if you do not make the time to have individually discussions– regardless of your structure’s in some cases stiff timeboxes.
Imagination can likewise be supported at a preparation level Invest the additional effort and time to structure legendaries with higher-level objectives to make sure that individuals aren’t constrained, even if that develops more screening and shipment obstacles later on.
Accepting Intentional Modification
There’s never ever an ideal time for modification. In unpredictable times, the risks provided by the danger of failure end up being more intense, and business wish to stick to what they understand. And in times of plenty, institutional momentum weighs versus accepting imagination, as danger is viewed to be unneeded, and business wish to stick to what works– even if it does not really work all that well.
Often it can take a crisis to tip this balance, as the status quo stops working to provide and the danger of modification is eclipsed by the pledge of chance as a method forward. However you must not wait on a state of desperation to make substantial choices. Rather, accept danger as a part of the advancement procedure in excellent times and bad, in order to make the most of chance with focus, resources, and consideration. A item supervisor who serves as a champ of danger, and believes huge, can take the chances that originate from venturing outside the Agile environment– blazing a trail on innovative efforts and offering a view of the entire forest.